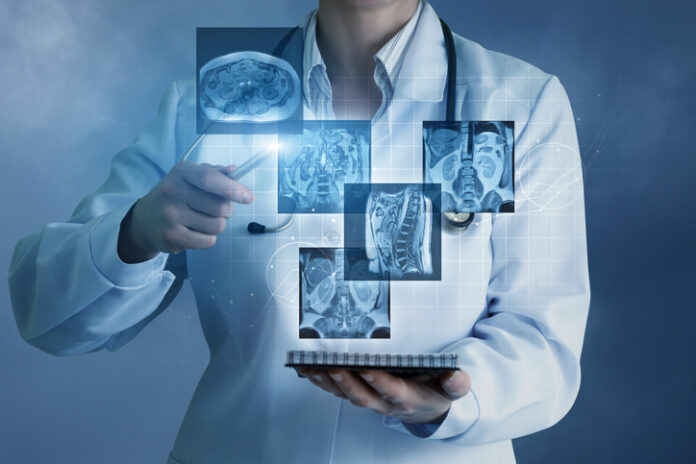
Radiology and medical imaging are both critical in healthcare. While the two techniques share many similarities, they also have some crucial differences. This article will explore the key differences between radiology and medical imaging and explain how they are used in healthcare. However, if you need more information on these topics, please visit amimaging.com. It is an excellent resource for anyone interested in learning more about radiology and medical imaging.
Now, let’s take a closer look at what sets radiology and medical imaging apart.
Radiology versus Medical Imaging
Medical imaging refers to the various technologies used to view the body’s internal structures. These techniques include x-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound.
On the other hand, radiology is the branch of medicine that deals with imaging and radiation technology to diagnose and treat diseases. In this regard, a radiologist is a medical expert who can use and interpret medical images to make a diagnosis or aid in monitoring and treating a patient’s condition.
There are two branches of radiology:
Diagnostic Radiology – Diagnostic radiology involves observing the body’s internal structures using imaging techniques.
Interventional radiology – In intervention radiology, the medical expert uses imaging tools to help perform minimally invasive procedures, such as inserting catheters, to help in treating health conditions.
Now let’s have a detailed look at some medical imaging techniques.
X-Rays
X-rays are ionizing radiation that can penetrate the body, allowing radiologists to create images of the body’s internal organs. Because of their quick results, X-rays are pretty common in medical settings. In addition, X-rays are relatively safe due to their low radiation levels. The safety of X-rays and their inexpensive cost make them popular options for imaging bones, joints, and spinal damage.
Advances in this technology have brought in digital X-rays, which provide comparably higher resolution images than traditional X-rays while utilizing lower radiation levels.
CT Scans
Computed tomography, or CT scans, use multiple X-ray images to create 3D images. This feature allows them to deliver comparably more detailed images than X-rays. Like X-rays, CT scans will expose you to low levels of radiation. So they are relatively safe and quick too. CT scans are often used for the following:
- Assessing heart and vascular conditions
- Demonstrating injuries from traumas, such as car accidents
- Detecting cancers
- Guiding biopsies and other minimally invasive procedures
MRI Scans
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI scans, utilize a magnetic field and radio waves to display 3D images of internal structures of the body. This imaging mode does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe option. MRI scans provide even more detailed images, making them ideal for:
- Detecting tumors
- Diagnosing injuries to tendons, ligaments, and muscles
- Evaluating the brain and spinal cord
- evaluating strokes
- Screening for breast cancer
Ultrasound
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a medical imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of internal body structures. The ultrasound is a safe and painless procedure that starts with a medical imaging expert applying a gel to the desired body area before placing a small probe called a transducer against your skin.
The probe enables the ultrasound to give real-time images of internal body parts. Like MRI and CT scans, this technique is also relatively safe and has applications in:
- diagnosis of fetal abnormalities
- Detecting organ damage
- Monitoring pregnancies
- diagnosis of breast lumps
Mammography
Mammography is a type of X-ray imaging used to screen for breast cancer in women. This technique is quite effective in the early detection of breast cancer, leading to better treatment options and higher survival rates.
Mammography works by taking X-rays of the breast tissue from different angles to give a detailed image of any abnormal growths.
PET Scans
Positron emission tomography, or PET scans, is a medical imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to help create detailed imagery of the body’s internal organs. Before the scan, a small amount of radioactive tracer is injected into the patient’s vein. The tracer will then travel through the body and be taken up by cells.
The PET scan can create images from the radiation the tracer emits. PET Scan can diagnose or monitor:
- Epilepsy
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cancerous tumors
- Heart and vascular diseases
Understanding the difference between radiology and medical imaging requires understanding the techniques involved. Some key imaging techniques include x-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound. While each of these technologies has its unique advantages, they all provide valuable insight into the body’s internal structures, allowing medical professionals to diagnose and treat various diseases and conditions. Whether you are looking for diagnostic information or treatment options, medical imaging can help.